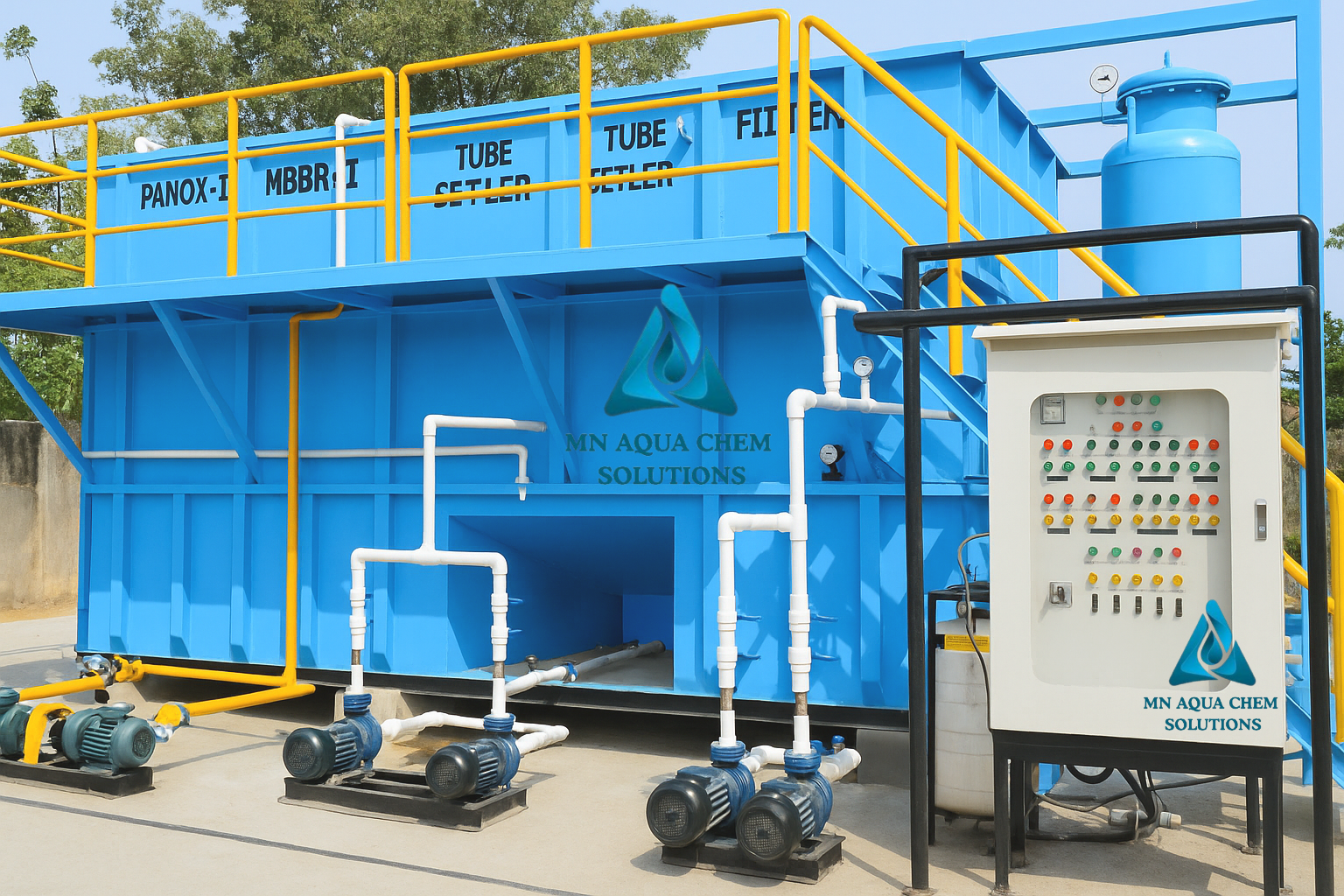
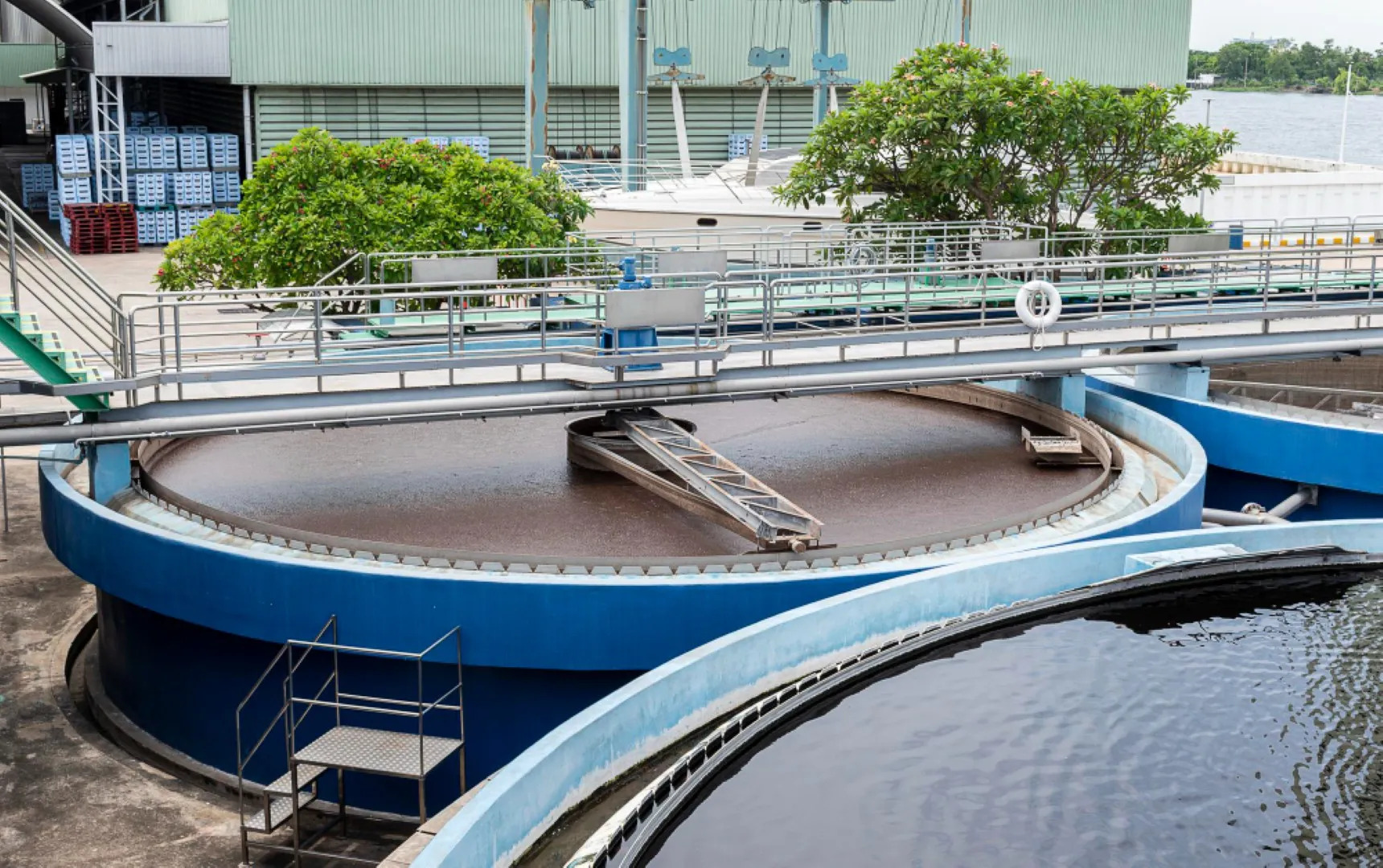
How water is treated with the help of STP and ETP plant

Wastewater treatment is mainly carried out through two major methods:
- STP (Sewage Treatment Plant)
- ETP (Effluent Treatment Plant)
Both treat wastewater but differ in the type of water treated and end-use.
1. STP (Sewage Treatment Plant)
STP is used for treating domestic wastewater generated from residential buildings, apartments, hotels, hospitals, offices, and institutions.
Sources of Sewage:
- Black Water → Wastewater from toilets (contains fecal matter, urine, pathogens, organic matter, nitrogen, phosphorus).
- Gray Water → Wastewater from bathrooms, washbasins, kitchens, laundry (less contaminated, contains soap, grease, detergents).
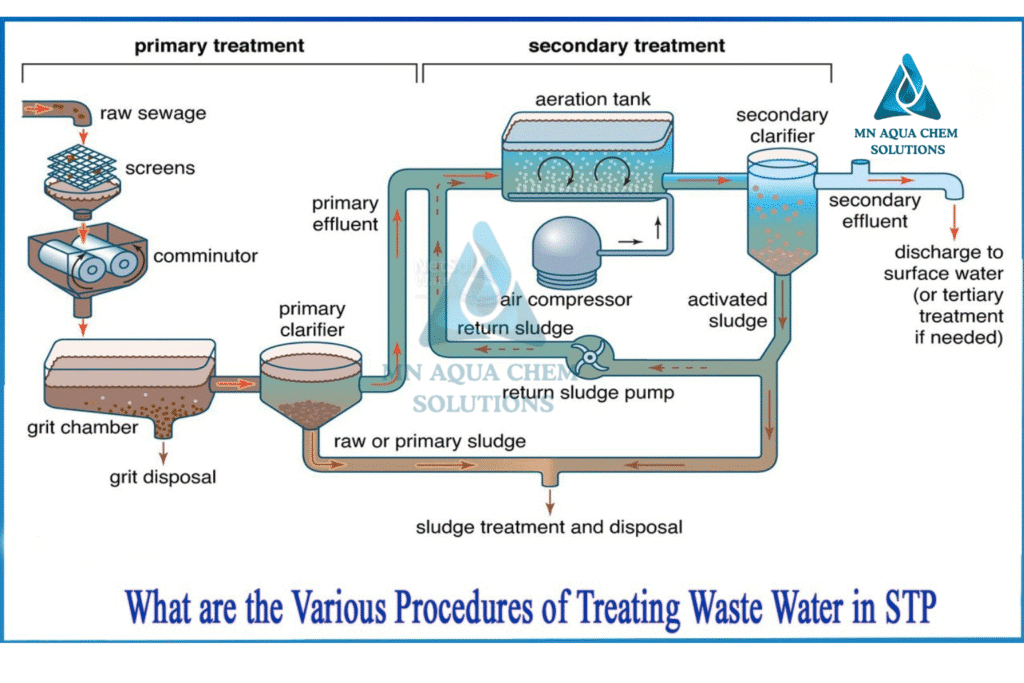
STP Treatment Process:
- Preliminary Treatment
- Screening, grit removal, oil & grease trap.
- Removes plastics, rags, stones, sand.
- Primary Treatment
- Sedimentation tanks allow suspended solids to settle.
- Produces primary sludge.
- Secondary Treatment (Biological)
- Aeration Tank / MBBR / SBR: Microorganisms break down organic matter (BOD, COD reduction).
- Secondary clarifier separates biomass (activated sludge).
- Tertiary Treatment
- Filtration (sand, carbon, UF membranes), disinfection (UV/chlorine/ozone).
- Produces clean water safe for reuse in flushing, gardening, cooling towers.
Key Point: STPs treat black water + gray water and make it reusable for non-potable purposes.

2. ETP (Effluent Treatment Plant)
ETP is used in industries to treat trade effluents before discharge/reuse.
Sources of Industrial Effluents:
- Trade Waste → Non-hazardous industrial wastewater (food processing waste, textile dye water, sugar mill effluents, paper pulp wastewater).
- Hazardous Effluents → Contains heavy metals, toxic chemicals, solvents, acids, alkalis, oils (from pharma, chemical plants, tanneries, electroplating, refineries).
ETP Treatment Process:
- Preliminary Treatment
- Screening, equalization, oil separation, neutralization.
- Primary Treatment
- Chemical coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation.
- Removes suspended solids, color, some metals.
- Secondary Treatment (Biological)
- Aerobic / anaerobic systems depending on wastewater.
- Reduces organic load (BOD, COD).
- Tertiary / Advanced Treatment
- Activated carbon, reverse osmosis, MEE (Multi-effect evaporator), stripping, advanced oxidation, membrane bioreactors.
- Removes toxic chemicals, heavy metals, dissolved salts.
Key Point: ETPs are designed to handle industrial hazardous effluents and comply with Pollution Control Board norms before discharge
Comparison – STP vs ETP
| Aspect | STP (Sewage Treatment Plant) | ETP (Effluent Treatment Plant) |
| Source of Wastewater | Domestic sewage (black water + gray water) | Industrial effluents (trade waste + hazardous effluents) |
| Contaminants | Organic waste, soap, grease, pathogens | Chemicals, heavy metals, dyes, oils, toxins |
| Treatment Focus | Biological + disinfection | Chemical + physical + biological + advanced |
| Reuse Options | Flushing, gardening, cooling tower, construction | Process reuse, safe discharge, zero liquid discharge |
| Regulation | CPCB & local municipal norms | CPCB & SPCB industrial effluent standards |
In Short:
- STP → Treats sewage from toilets, kitchens, bathrooms (black water + gray water).
- ETP → Treats industrial wastewater (trade waste + hazardous effluents).
Looking for a reliable partner in wastewater management? MN Aqua Chem Solutions specializes in STP (Sewage Treatment Plants) and ETP (Effluent Treatment Plants) with advanced technologies like MBBR, SBR, and MBR, catering from 5 KLD to 2000 KLD. From design and installation to operation, maintenance, and chemical supply, we provide end-to-end solutions tailored for residential, commercial, and industrial needs. With local support, quick service, and compliance assurance, MN Aqua Chem ensures sustainable, cost-effective, and efficient wastewater treatment. 💧




